Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMVP5YE)
| Drug Name |
Doxorubicin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
doxorubicin; 23214-92-8; Doxil; Doxorubicine; Adriablastin; Doxorubicinum; 14-Hydroxydaunomycin; 14-Hydroxydaunorubicine; Doxorubicina; Adriamycin semiquinone; Doxorubicinum [INN-Latin]; Doxorubicine [INN-French]; Doxorubicina [INN-Spanish]; Myocet; FI 106; Doxorubicin [USAN:INN:BAN]; CCRIS 739; NDC 38242-874; HSDB 3070; UNII-80168379AG; NCI-C01514; EINECS 245-495-6; CHEMBL53463; CHEBI:28748; 5,12-Naphthacenedione,; ADM; ADR; ThermoDox; Aerosolized Doxorubicin; Doxorubicin citrate; RDF Rubex; Conjugate of doxorubicin with humanized monoclonal antibody LL1 against CD74; DM2; JT9100000; Adiblastine (hydrochloride salt); Adr iablatina (hydrochloride salt); Adriablastine (hydrochloride salt); Adriablatina (hydrochloride salt); Adriacin (hydrochloride salt); Adriamycin PFS (TN); Adriamycin PFS (hydrochloride salt); Adriamycin RDF (TN); Adriamycin RDF (hydrochloride salt); Adriblastina (TN); Adriblastina (hydrochloride salt); Adriblatina (hydrochloride salt); Caelyx (TN); Conjugate of doxorubicin with monoclonal antibody P4/D10 against GP120; DOX-SL; Doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydrochloride salt); Doxorubicin-hLL1; Doxorubicin-hLL1 conjugate; Farmablastina (hydrochloride salt); Hydroxydaunomycin hydrochlor ide (hydrochloride salt); Hydroxydaunomycin hydrochloride (hydrochloride salt); Hydroxydaunorubicin hydrochloride (hydrochloride salt); Myocet (TN); Rubex (TN); Rubex (hydrochloride salt); TLC D-99; Doxorubicin (USAN/INN); Doxorubicin-P4/D10; Doxorubicin-P4/D10 conjugate; Cantide + adriamycin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
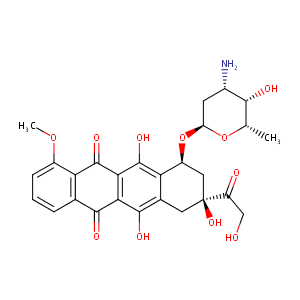 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 3 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 543.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Doxorubicin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Doxorubicin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
| DIG |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Formulation |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | Doxorubicin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7069). | ||||
| 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02112656) Study of ThermoDox With Standardized Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) (OPTIMA). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| 4 | Antitumor activity of liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin in advanced breast cancer: phase II study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Nov 7;82(21):1706-10. | ||||
| 5 | Design and development of antisense drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2008 3(10):1189-1207. | ||||
| 6 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 7 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 8 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 9 | Recommendations for genetic testing to reduce the incidence of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;82(3):683-95. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13008. Epub 2016 Jun 30. | ||||
| 10 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 11 | Genome-wide association study of chemotherapeutic agent-induced severe neutropenia/leucopenia for patients in Biobank Japan. Cancer Sci. 2013 Aug;104(8):1074-82. doi: 10.1111/cas.12186. Epub 2013 Jun 10. | ||||
| 12 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 13 | ABCB8 mediates doxorubicin resistance in melanoma cells by protecting the mitochondrial genome. Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Jan;7(1):79-87. | ||||
| 14 | ABCB5-mediated doxorubicin transport and chemoresistance in human malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 2005 May 15;65(10):4320-33. | ||||
| 15 | Influence of pharmacogenetics on response and toxicity in breast cancer patients treated with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Br J Cancer. 2010 Mar 16;102(6):1003-9. | ||||
| 16 | Circadian rhythms in gene expression: Relationship to physiology, disease, drug disposition and drug action. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Jul 31;62(9-10):904-17. | ||||
| 17 | Involvement of the drug transporters p glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein Mrp2 in telithromycin transport. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jan;50(1):80-7. | ||||
| 18 | The role of bioreductive activation of doxorubicin in cytotoxic activity against leukaemia HL60-sensitive cell line and its multidrug-resistant sublines. Br J Cancer. 2005 Jul 11;93(1):89-97. | ||||
| 19 | Doxorubicin transport by RALBP1 and ABCG2 in lung and breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2007 Mar;30(3):717-25. | ||||
| 20 | MDR1 (ABCB1) G1199A (Ser400Asn) polymorphism alters transepithelial permeability and sensitivity to anticancer agents. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;64(1):183-8. | ||||
| 21 | Expression levels and activation of a PXR variant are directly related to drug resistance in osteosarcoma cell lines. Cancer. 2007 Mar 1;109(5):957-65. | ||||
| 22 | Inhibitory effects of anticancer drugs on dextromethorphan-O-demethylase activity in human liver microsomes. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1993;32(6):491-5. | ||||
| 23 | Drug related genetic polymorphisms affecting adverse reactions to methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin and cisplatin in patients with urothelial cancer. J Urol. 2008 Dec;180(6):2389-95. | ||||
| 24 | Differential ability of cytostatics from anthraquinone group to generate free radicals in three enzymatic systems: NADH dehydrogenase, NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase, and xanthine oxidase. Oncol Res. 2003;13(5):245-52. | ||||
| 25 | The role of nitric oxide in anthracycline toxicity and prospects for pharmacologic prevention of cardiac damage. FASEB J. 2004 Apr;18(6):664-75. | ||||
| 26 | Kinetics of anthracycline antibiotic free radical formation and reductive glycosidase activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 May;223(1):68-75. | ||||
| 27 | Inactivation of the anticancer drugs doxorubicin and oracin by aldo-keto reductase (AKR) 1C3. Toxicol Lett. 2008 Sep;181(1):1-6. | ||||
| 28 | Carbonyl reductase 1 is a predominant doxorubicin reductase in the human liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Oct;36(10):2113-20. | ||||
| 29 | Xanthine oxidoreductase in drug metabolism: beyond a role as a detoxifying enzyme. Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(35):4027-4036. | ||||
| 30 | Differences in the efficiency of reductive activation of methionine synthase and exogenous electron acceptors between the common polymorphic variants of human methionine synthase reductase. Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 12;41(45):13378-85. | ||||
| 31 | Naturally occurring variants of human aldo-keto reductases with reduced in vitro metabolism of daunorubicin and doxorubicin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Dec;335(3):533-45. | ||||
| 32 | Bacterial inactivation of the anticancer drug doxorubicin. Chem Biol. 2012 Oct 26;19(10):1255-64. | ||||
| 33 | Transformation of the anticancer drug doxorubicin in the human gut microbiome. ACS Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 12;4(1):68-76. | ||||
| 34 | Bringing in vitro analysis closer to in vivo: studying doxorubicin toxicity and associated mechanisms in 3D human microtissues with PBPK-based dose modelling. Toxicol Lett. 2018 Sep 15;294:184-192. | ||||
| 35 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 36 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 37 | Doherty MM, Charman WN "The mucosa of the small intestine: how clinically relevant as an organ of drug metabolism?" Clin Pharmacokinet 41 (2002): 235-53. [PMID: 11978143] | ||||
| 38 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 39 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Tibsovo (ivosidenib). Agios Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Xospata (gilteritinib). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 44 | Bengtsson B, Fagerstrom PO "Extrapulmonary effects of terbutaline during prolonged administration." Clin Pharmacol Ther 31 (1982): 726-32. [PMID: 7042176] | ||||
| 45 | Ball P "Quinolone-induced QT interval prolongation: a not-so-unexpected class effect." J Antimicrob Chemother 45 (2000): 557-9. [PMID: 10797074] | ||||
| 46 | Bailey DG, Dresser GR, Kreeft JH, Munoz C, Freeman DJ, Bend JR "Grapefruit-felodipine interaction: Effect of unprocessed fruit and probable active ingredients." Clin Pharmacol Ther 68 (2000): 468-77. [PMID: 11103749] | ||||
| 47 | Iannini PB "Cardiotoxicity of macrolides, ketolides and fluoroquinolones that prolong the QTc interval." Expert Opin Drug Saf 1 (2002): 121-8. [PMID: 12904146] | ||||
| 48 | Johnson EJ, MacGowan AP, Potter MN, et al "Reduced absorption of oral ciprofloxacin after chemotherapy for haematological malignancy." J Antimicrob Chemother 25 (1990): 837-42. [PMID: 2373666] | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Balversa (erdafitinib). Janssen Products, LP, Horsham, PA. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Tukysa (tucatinib). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Daurismo (glasdegib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Adriamycin PFS (doxorubicin). Pharmacia and Upjohn, Kalamazoo, MI. | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 55 | Product Information. Serzone (nefazodone). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 56 | Product Information. Austedo (deutetrabenazine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Ingrezza (valbenazine). Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA. | ||||
| 58 | EMEA. European Medicines Agency "EPARs. European Union Public Assessment Reports.". | ||||
| 59 | Product Information. Tazverik (tazemetostat). Epizyme, Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 60 | Auclair B, Berning SE, Huitt GA, Peloquin CP "Potential interaction between itraconazole and clarithromycin." Pharmacotherapy 19 (1999): 1439-44. [PMID: 10600094] | ||||
| 61 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 62 | Anson BD, Weaver JG, Ackerman MJ, et al. "Blockade of HERG channels by HIV protease inhibitors." Lancet 365 (2005): 682-686. [PMID: 15721475] | ||||
| 63 | Product Information. Prezista (darunavir). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 64 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 65 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 66 | Product Information. Givlaari (givosiran). Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 67 | Product Information. Orladeyo (berotralstat). BioCryst Pharmaceuticals Inc, Durham, NC. | ||||
| 68 | Product Information. Prolia (denosumab). Amgen USA, Thousand Oaks, CA. | ||||
| 69 | Product Information. Xalkori (crizotinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 70 | Product Information. Vizimpro (dacomitinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 71 | Product Information. Tagrisso (osimertinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 72 | Product Information. Tabrecta (capmatinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 73 | Abernethy DR, Wesche DL, Barbey JT, et al. "Stereoselective halofantrine disposition and effect: concentration-related QTc prolongation." Br J Clin Pharmacol 51 (2001): 231-7. [PMID: 11298069] | ||||
| 74 | Harper KM, Knapp DJ, Criswell HE, Breese GR "Vasopressin and alcohol: A multifaceted relationship." Psychopharmacology (Berl) 235 (2018): 3363-79. [PMID: 32936259] | ||||
| 75 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 76 | Product Information. Copiktra (duvelisib). Verastem, Inc., Needham, MA. | ||||
| 77 | Ohnishi K, Yoshida H, Shigeno K, et al. "Prolongation of the QT interval and ventricular tachycardia in patients treated with arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia." Ann Intern Med 133 (2000): 881-5. [PMID: 11103058] | ||||
| 78 | Product Information. Braftovi (encorafenib). Array BioPharma Inc., Boulder, CO. | ||||
| 79 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 80 | Product Information. Farydak (panobinostat). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 81 | Bennett CL, Nebeker JR, Samore MH, et al "The Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports (RADAR) project." JAMA 293 (2005): 2131-40. [PMID: 15870417] | ||||
| 82 | Product Information. Vumerity (diroximel fumarate). Alkermes, Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 83 | Product Information. Gilenya (fingolimod). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 84 | Product Information. Ocrevus (ocrelizumab). Genentech, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 85 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 86 | Product Information. Synribo (omacetaxine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 87 | Product Information. Varubi (rolapitant). Tesaro Inc., Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 88 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 89 | Product Information. Nuplazid (pimavanserin). Accelis Pharma, East Windsor, NJ. | ||||
| 90 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 91 | Product Information. Macrilen (macimorelin). Aeterna Zentaris, Charleston, SC. | ||||
| 92 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 93 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 94 | Product Information. Nubeqa (darolutamide). Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ. | ||||
| 95 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 96 | Ansari SR, Chopra N "Gatifloxacin and Prolonged QT Interval." Am J Med Sci 327 (2004): 55-6. [PMID: 14722399] | ||||
| 97 | Product Information. Arcalyst (rilonacept). Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc, Tarrytown, NY. | ||||
| 98 | Product Information. Cimzia (certolizumab). UCB Pharma Inc, Smyrna, GA. | ||||
| 99 | Product Information. Barhemsys (amisulpride). Acacia Pharma, Inc, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 100 | CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/ "Recommendations of the advisory committtee on immunization practices (ACIP): use of vaccines and immune globulins in persons with altered immunocompetence." MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 42(RR-04) (1993): 1-18. [PMID: 20300058] | ||||
| 101 | Product Information. Oxbryta (voxelotor). Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc., South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 102 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 103 | Goto M, Sato M, Kitzazawa H, et.al "Papaverine-induced QT interval prolongation and ventricular fibrillation in a patient with a history of drug-induced QT prolongation." Intern Med 53 (2014): 1629-31. [PMID: 25088875] | ||||
